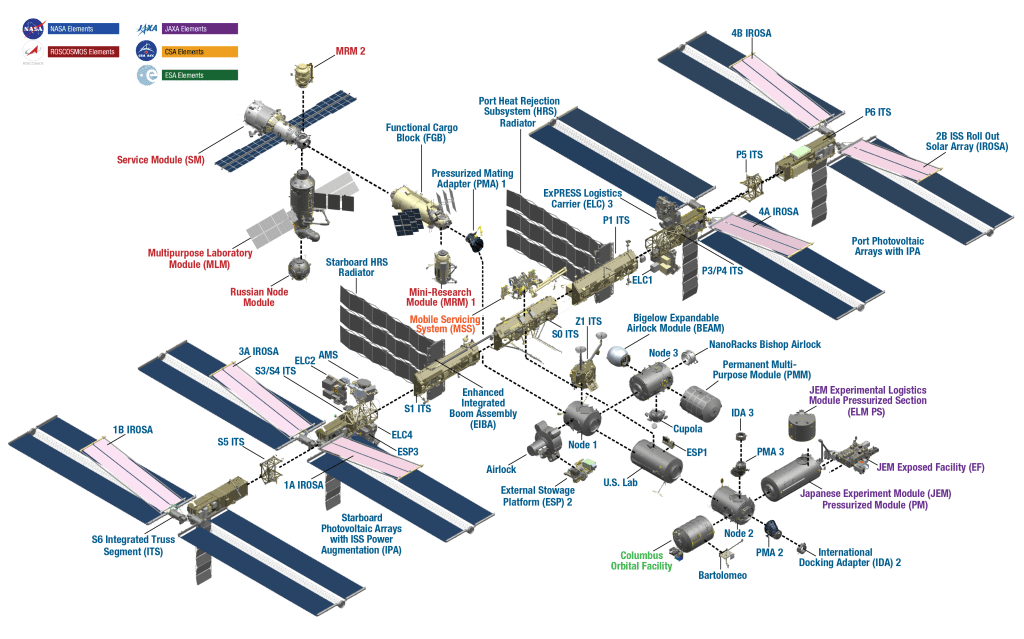
The International Space Center: A Gateway to the Stars
The International Space Center (ISC) stands as a testament to human ingenuity, collaboration, and the unending quest for exploration beyond our planet. Orbiting high above Earth, this remarkable structure serves as a hub for scientific research, technological innovation, and international cooperation in space exploration.
History of the ISC
The idea for an international space station was first proposed in the early days of space exploration. In 1998, construction began on what would eventually become the largest human-made structure in space. Over the years, multiple countries have contributed modules and resources to the ISC, creating a truly global endeavor.
Mission and Objectives
The primary mission of the ISC is to conduct scientific research in microgravity conditions. This unique environment allows scientists to study phenomena that are impossible to replicate on Earth, leading to groundbreaking discoveries in fields such as biology, physics, and materials science.
Besides scientific research, the ISC also serves as a platform for international cooperation in space exploration. Astronauts from various countries live and work together on the station, fostering cross-cultural understanding and collaboration in pursuit of common goals.
Life on Board
Living aboard the ISC is no easy feat. Astronauts must adapt to microgravity conditions, perform daily tasks in cramped quarters, and maintain a rigorous schedule of scientific experiments and maintenance activities. Despite these challenges, astronauts speak of the awe-inspiring views of Earth from space and the camaraderie that develops among crew members.
Future of Space Exploration
As we look to the future, the ISC represents just one step in humanity’s journey into space. Plans are already underway for future space stations, lunar bases, and crewed missions to Mars. The knowledge gained from our experiences on the ISC will be crucial in shaping these future endeavors.
In conclusion, the International Space Center stands as a beacon of human achievement and cooperation in space exploration. It serves as a reminder of what we can accomplish when we work together towards a common goal: reaching for the stars.
9 Benefits of the International Space Center: Advancing Science, Cooperation, and Inspiration
- Facilitates groundbreaking scientific research in microgravity conditions.
- Serves as a platform for international cooperation in space exploration.
- Provides valuable insights into biology, physics, and materials science.
- Offers astronauts unparalleled views of Earth from space.
- Fosters cross-cultural understanding among crew members from different countries.
- Contributes to technological innovation in the field of space exploration.
- Acts as a testing ground for future long-duration space missions.
- Demonstrates the potential for peaceful collaboration on a global scale.
- Inspires future generations to pursue careers in science and engineering.
Challenges Facing the International Space Station: Costs, Risks, and Political Hurdles
- High cost of construction and maintenance
- Limited living space for astronauts
- Dependence on international cooperation, which can be politically challenging
- Risks of accidents or malfunctions in the harsh environment of space
- Health risks to astronauts from prolonged exposure to microgravity
- Potential for space debris collisions, endangering the station and its crew
Facilitates groundbreaking scientific research in microgravity conditions.
The International Space Center plays a pivotal role in facilitating groundbreaking scientific research in microgravity conditions. By providing a unique environment that is impossible to replicate on Earth, the ISC enables scientists to conduct experiments that lead to revolutionary discoveries in various fields such as biology, physics, and materials science. This invaluable opportunity to study phenomena in microgravity opens up new frontiers of knowledge and understanding, pushing the boundaries of human exploration and innovation in ways that would not be possible without the presence of the space station.
Serves as a platform for international cooperation in space exploration.
The International Space Center serves as a vital platform for fostering international cooperation in the realm of space exploration. By bringing together astronauts, scientists, and engineers from various countries to live and work together in the unique environment of space, the ISC promotes collaboration, shared knowledge, and cultural exchange on a global scale. This collaborative effort not only advances scientific research and technological innovation but also strengthens diplomatic ties between nations, demonstrating the power of unity in pursuit of common goals beyond the boundaries of Earth.
Provides valuable insights into biology, physics, and materials science.
The International Space Center serves as a vital platform for conducting scientific research in microgravity conditions, offering invaluable insights into the fields of biology, physics, and materials science. By studying phenomena in space that cannot be replicated on Earth, researchers are able to make groundbreaking discoveries that have the potential to revolutionize our understanding of these disciplines. The unique environment of the ISC enables experiments that lead to new knowledge and advancements in various scientific fields, paving the way for future innovations and technological developments on Earth and beyond.
Offers astronauts unparalleled views of Earth from space.
The International Space Center offers astronauts an unparalleled opportunity to witness breathtaking views of Earth from space. Floating high above our planet, astronauts aboard the ISC are treated to awe-inspiring vistas of continents, oceans, and weather patterns unlike anything seen from the ground. These panoramic views not only provide a sense of wonder and appreciation for the beauty of our planet but also offer valuable insights into Earth’s ecosystems, climate dynamics, and geological features that can only be fully grasped from the unique vantage point of space.
Fosters cross-cultural understanding among crew members from different countries.
The International Space Center fosters cross-cultural understanding among crew members from different countries by providing a unique environment where individuals must collaborate, communicate, and live together in close quarters while working towards common goals. This shared experience of overcoming challenges and exploring the wonders of space creates strong bonds that transcend cultural differences, promoting mutual respect, empathy, and a deeper appreciation for diversity. As astronauts from various nations work side by side on the ISC, they not only advance scientific knowledge but also exemplify the power of cooperation and unity on a global scale.
Contributes to technological innovation in the field of space exploration.
The International Space Center plays a pivotal role in driving technological innovation in the realm of space exploration. Through its cutting-edge research and experiments conducted in microgravity conditions, the ISC pushes the boundaries of scientific knowledge and fosters the development of new technologies that benefit not only space exploration but also various industries on Earth. By tackling challenges unique to space environments, the ISC inspires advancements in robotics, materials science, life support systems, and more, paving the way for groundbreaking innovations that have far-reaching implications for humanity’s future endeavors in outer space.
Acts as a testing ground for future long-duration space missions.
The International Space Center serves as a vital testing ground for future long-duration space missions, providing invaluable insights into the challenges and opportunities of extended stays in space. Astronauts living aboard the ISC undergo rigorous training and conduct experiments that simulate the conditions of long-duration missions, helping to develop the technologies, protocols, and strategies needed for successful exploration beyond Earth’s orbit. By pushing the boundaries of human endurance in space, the ISC paves the way for ambitious missions to the Moon, Mars, and beyond, ensuring that we are well-prepared for the challenges that lie ahead in our quest for further exploration of the cosmos.
Demonstrates the potential for peaceful collaboration on a global scale.
The International Space Center exemplifies the potential for peaceful collaboration on a global scale by bringing together nations from around the world to work towards a common goal of advancing scientific knowledge and exploration beyond Earth’s boundaries. Through shared resources, expertise, and cultural exchange, the ISC showcases how countries can set aside differences and come together in harmony to achieve incredible feats in space exploration. This spirit of cooperation not only benefits the scientific community but also serves as a powerful symbol of unity and peace among nations, demonstrating that when we work together towards a shared vision, remarkable achievements become possible.
Inspires future generations to pursue careers in science and engineering.
The International Space Center serves as a powerful beacon of inspiration for future generations, igniting a passion for science and engineering in young minds around the world. By showcasing the incredible achievements and groundbreaking research conducted aboard the station, the ISC motivates aspiring scientists and engineers to pursue careers in space exploration and related fields. The collaborative nature of the ISC also highlights the importance of international cooperation in pushing the boundaries of human knowledge, encouraging young individuals to work together towards common goals for the betterment of humanity and our understanding of the universe.
High cost of construction and maintenance
The International Space Center faces a significant challenge due to the high cost of construction and maintenance. Building and sustaining a structure in the harsh environment of space requires substantial financial investment, with expenses escalating for repairs, upgrades, and resupply missions. The cost of transporting materials and equipment to the station adds to the financial burden, making it a constant concern for the countries involved in its operation. Balancing the need for cutting-edge technology and safety measures with budget constraints poses a complex dilemma for the ISC’s sustainability in the long term.
Limited living space for astronauts
One significant challenge faced by astronauts aboard the International Space Center is the limited living space available to them. In the microgravity environment of the ISS, every inch of space is carefully utilized, leaving little room for personal privacy or relaxation. Astronauts must adapt to confined quarters for sleeping, eating, exercising, and conducting experiments, which can lead to feelings of claustrophobia and stress during long-duration missions. Despite the innovative design solutions implemented to maximize space efficiency, the lack of ample living space remains a con that astronauts must contend with as they carry out their demanding tasks in orbit.
Dependence on international cooperation, which can be politically challenging
One significant con of the International Space Center is its dependence on international cooperation, which can be politically challenging. The involvement of multiple countries in the project means that decisions regarding funding, research priorities, and crew assignments must navigate complex diplomatic relationships and differing national interests. Political tensions between participating nations can sometimes impede progress or lead to disagreements on crucial issues, potentially jeopardizing the smooth operation and long-term sustainability of the ISC. This reliance on international collaboration introduces a layer of complexity that requires constant negotiation and compromise to ensure the continued success of this remarkable space station.
Risks of accidents or malfunctions in the harsh environment of space
One significant con of the International Space Center is the inherent risks associated with accidents or malfunctions in the unforgiving environment of space. The extreme conditions of space, including microgravity, cosmic radiation, and temperature variations, pose constant challenges to the safety and functionality of the station. Any technical failure or human error could have catastrophic consequences for the astronauts onboard and jeopardize ongoing research activities. The need for meticulous planning, rigorous maintenance protocols, and swift response to emergencies is paramount to mitigate these risks and ensure the continued operation of the International Space Center.
Health risks to astronauts from prolonged exposure to microgravity
Prolonged exposure to microgravity poses a significant health risk to astronauts aboard the International Space Center. The absence of gravity in space can lead to muscle atrophy, bone density loss, cardiovascular deconditioning, and fluid shifts in the body. These physiological changes can have long-term implications for astronaut health, potentially impacting their ability to perform tasks both in space and upon returning to Earth. Mitigating these health risks through exercise regimens, specialized equipment, and medical monitoring is crucial to ensure the well-being of astronauts during extended missions aboard the International Space Center.
Potential for space debris collisions, endangering the station and its crew
One significant con of the International Space Center is the potential for space debris collisions, which poses a serious threat to the station and its crew. With thousands of defunct satellites, rocket fragments, and other debris orbiting Earth at high speeds, there is a constant risk of impact that could cause catastrophic damage to the station. Even small pieces of debris can create dangerous situations, jeopardizing the safety of astronauts and the integrity of the structure itself. Mitigating this risk requires constant monitoring and maneuvering to avoid potential collisions, highlighting the ongoing challenge of operating in Earth’s crowded orbital environment.